Stages of the Analytics Life Cycle
Across industries, the applied use of data to inform business decisions has become a foundational (arguably critical) element of business. The end goal is to ultimately derive actionable insights from vast amounts of data being collected but it takes a series of activities/tasks to arrive at this juncture. Here is a description of each stage of the analytics life cycle:
- Data Acquisition – This may involve scraping data, interfacing with APIs, querying relational and non-relational databases, or defining strategy in relation to what data to pursue.
- Data Cleaning/Transformation – This may involve parsing and aggregating messy, incomplete, and unstructured data sources to produce datasets that can be used in analytics and/or predictive modeling.
- Analytics – This involves statistical and machine learning-based modeling in order to understand, describe, or predict patterns in the data.
- Prescribing Actions – This involves interpreting analytical results through the lens of business priorities, and using data-driven insights to inform strategy.
- Programming/Automation – In many cases, data scientists are responsible for creating libraries and utilities to operationalize or simplify various stages of this process. Often, they will contribute production-level code for a firm’s data products.
*Source: Burtch Works
Big Data Analytics Lifecycle
Big Data analysis differs from traditional data analysis primarily due to the volume, velocity, and variety of characteristics for the data being processed. This is a helpful overview I found on the high-level steps involved with acquiring, processing, analyzing, and repurposing data with the end goal of performing Big Data analysis.
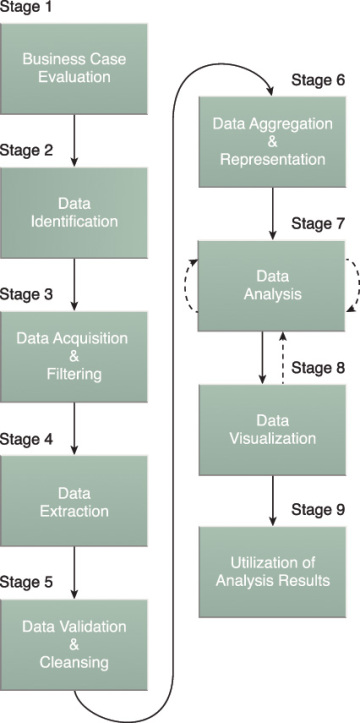
*Source: InformIT
About Me
I'm a data leader working to advance data-driven cultures by wrangling disparate data sources and empowering end users to uncover key insights that tell a bigger story. LEARN MORE >>
comments powered by Disqus